A cash book is a financial journal that contains all cash receipt inflows and payment outflows. Cash receipts include sales receipts from customers and interest income receipt. Outflows, on the other hand, include payments to suppliers and bank loan interest repayments. A cash book is a subsidiary to the general ledger in which all cash transactions during a period are recorded.
The company’s transactions are updated daily and in chronological order. In this way, it is easy to reference and transaction dates can be found quickly. The nature of transactions are also recorded alongside the amount of inflow and outflow in a separate column for reference checking as well. Another separate column tracks the running balance after each inflow or outflow.
The Advantages of a Cash Book
A cash book is regularly prepared by a company due to the several benefits and advantages it brings. Here are some of them:
A daily-updated cash book delivers precise info, helping companies when it comes to cash management.
The management will be aware of the updated cash balances instantly. They can analyse the trend of cash balances as well. An accurate cash book prevents overpayment to suppliers exceeding the cash balance.
If the management has excess cash sitting in the account, they can invest in short term deposits to earn higher rates instead of leaving excess funds idle in the bank account.
The preparation of cash book increases accounting efficiency.
For cash book recording, all cash transactions are recorded straight away in the form of a usable working ledger. This saves time and labour required for recording cash transactions in a journal. A cash book is a book of accounts which fulfils the objective of both journal and ledger.
A cash book preparation allows mistakes to be detected easily through verification because entries are kept up-to-date daily.
Since a cash book is balanced almost daily, frauds can be prevented. Discrepancies, if any, can be found and rectified instantly.
Cash Book Recording Features
All transactions in a cash book are placed in their respective section. All cash inflows are recorded on the left side as debit, and all cash outflows are recorded on the right side as credit.
The difference between the left and right sides would give the running cash balance. Positive would mean the company is in net cash flow positive position, while negative balance means negative cash flow position.
The cash book is set up in columns. The three common versions of the cash book used by companies are single-column, double-column, and triple-column versions. A single-column cash book shows only receipts and payments of cash. A double-column cash book shows details about bank transactions on top of regular receipts and payments. Finally, a triple column cash book shows all of the above as well as information about purchase or sales discounts.
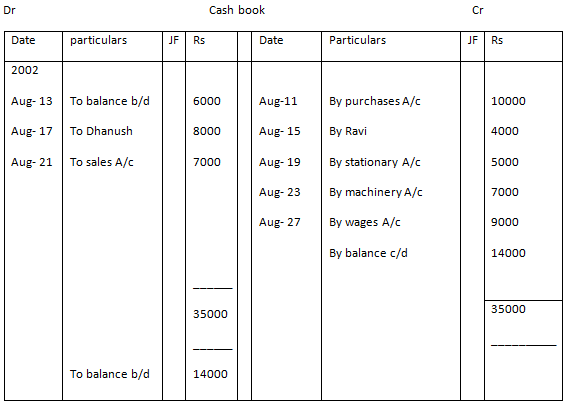
A single column cash book will typically have the column headers such as date, description, and amount. These headers are present for both “receipt” and “payment” side.
A cash book is updated continuously in chronological order by transaction. In the description column, a short and simple report of a transaction is written. In the reference column, the account number for the related general ledger account is placed. The transaction amount is recorded in the final column.
Conclusion
Every company, whether a small-medium enterprise or a large multinational corporation, needs to maintain accurate records of its day-to-day transactions. Cash is the lifeblood of a company. Therefore, monitoring cash flows is crucial to the growth of a business. The preparation of a cash book serves as an effective tool for monitoring company cash flows and greatly increases accounting efficiency.











Leave A Comment